Things You May Not Know About Stone (1)
In this issue, Xiaobian will mainly bring you the dry goods knowledge prepared by Sean Hou from three aspects: factory inspection/ore inspection, stone physical performance index and stone surface protection.

Things You May Not Know About Stone (2)
4
Factory inspection/ore inspection
Mine inspection process
I. Work contact letter (to the customer), informing the stone processing plant/stone mine to prepare
1. Stone processing plant:
① Stone samples;
② Plant introduction and equipment list.
2. Stone mine:
① Past inspection report of the stone to be selected;
(2) that stone is extract from the sampling point to be selecte, and the sample is processed;
③ Quarry plan (mark the sampling position).
II. Inspection record of stone processing plant
1. Plant overview:
① Factory name, address, scale, legal person, traffic and transportation;
② Plate-arranging site/watchtower.
2. Equipment list: block slicing, decorative surface processing, edge processing, edge slotting, back opening, special processing and protective treatment.
3. Human resources: management personnel, technical personnel, technical workers, QA/QC personnel and logistics personnel.
4. Comprehensive production capacity
5. Quality assurance system
6. Sample inspection: number, name, inspection record, defect record and inspection method.
III. Inspection record of quarry and opening site
1. Mine overview: mine name, address, reserves, legal person, traffic and transportation.
2. Mine preparation list: the past inspection report of the stone to be selected, the processed sample, and the quarry plan (mark the sampling position).
3. Inspection process and record: sample appearance, record and comparison of previous similar stone test data, sample number/signature/sealing, sample mailing, record of relevant information (sampling point location/ore bed/working platform, block size, sample quantity and specification, reserve determination, rough processing site/equipment, logistics equipment, human resources, QA/QC, annual output of rough board).
4. Others
IV. Investigation report of stone processing plant/mine
1. Overview
2. Background information
3. Inspection record
4. Comments and suggestions
5. Appendix
5
Physical performance index of stone
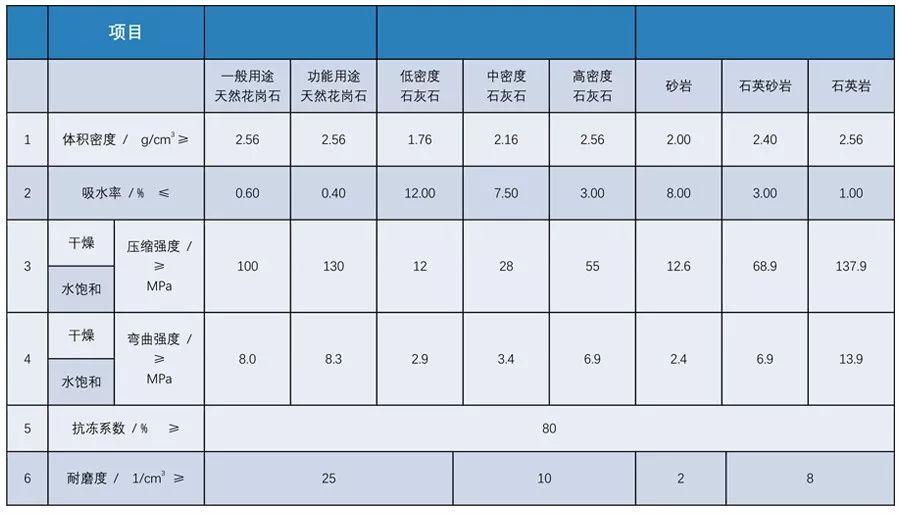
Conclusion:
(1) For projects with high quality requirements, the water absorption and bending strength of granite are recommended to adopt functional indicators;
(2) Sandstone, not all of which are "fragile";
(3) Facade stone in cold areas shall have the requirement of frost resistance coefficient;
(4) The stone used for the ground, stair steps, table top and other easily worn parts shall have wear resistance requirements.
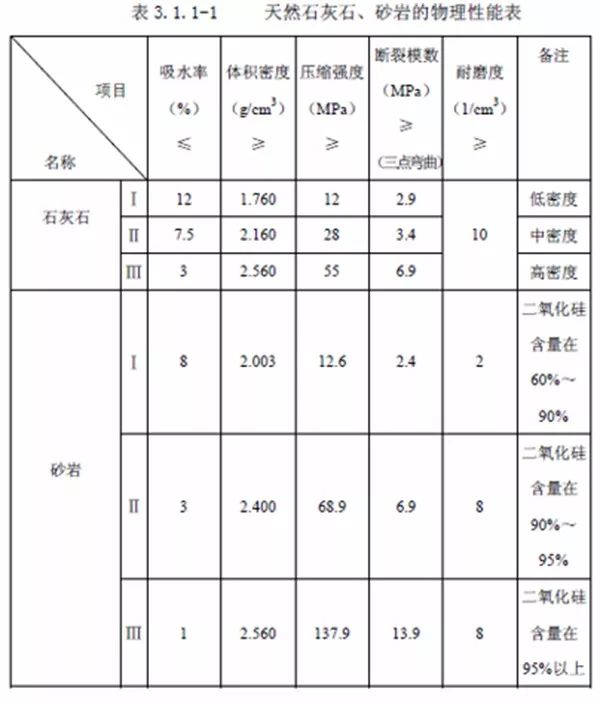
Some specifications of physical performance indexes of stone are extracted as follows:
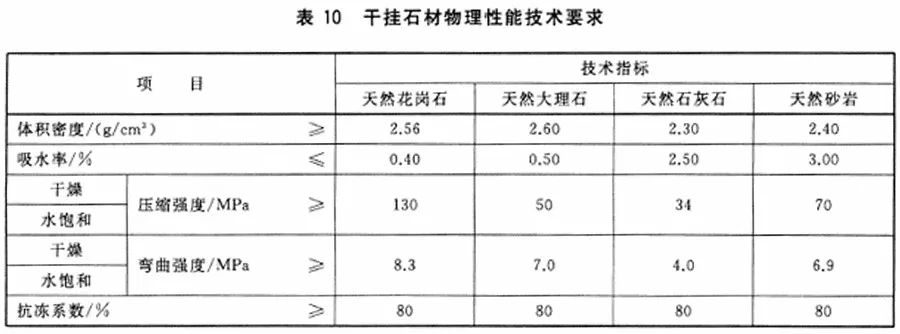
1. GB/T 32834-2016 Dry-hanging Facing Building Stone
6.8 Physical properties
6.8.1 The physical properties and technical indexes of dry-hanging stone shall conform to the provisions in Table 10.
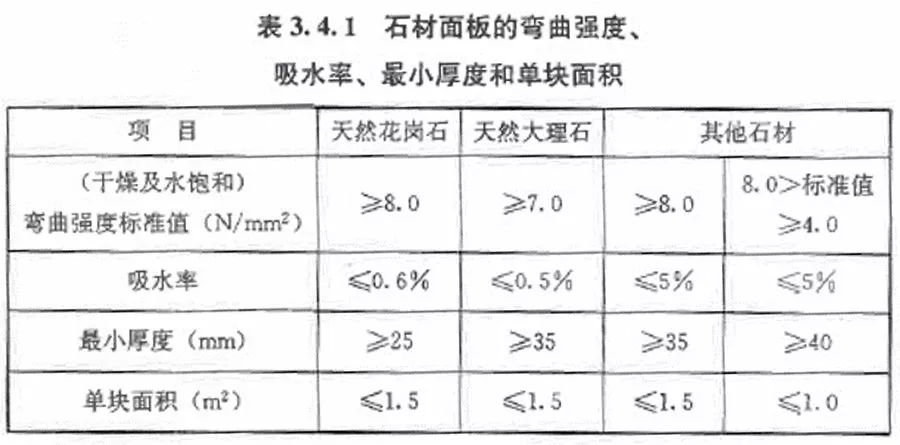
2. JGJ 321-2014 Technical Specification for Dot-hanging Exterior Wall Panel Engineering
3. JCG/T 60001-2007 Technical Specification for Natural Stone Decoration Engineering
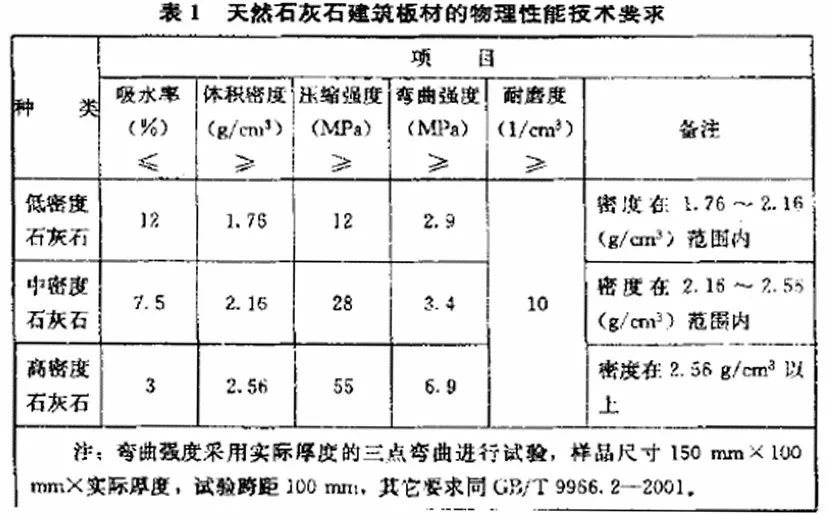
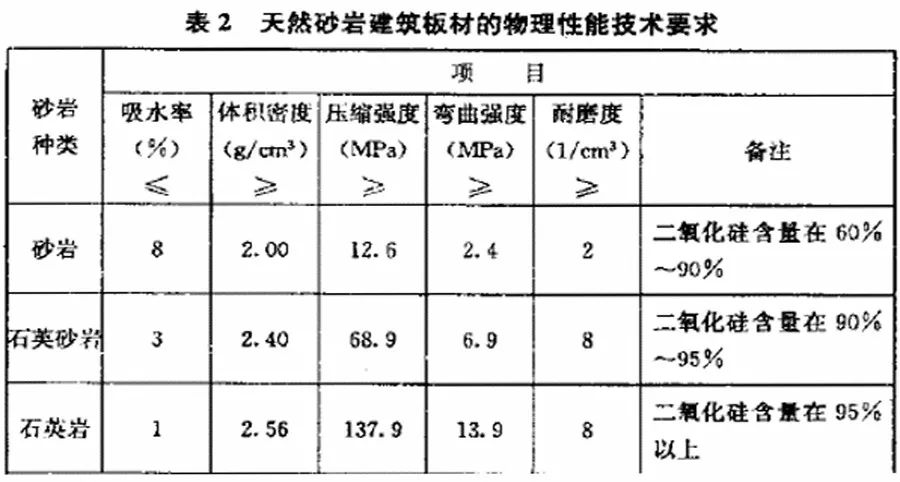
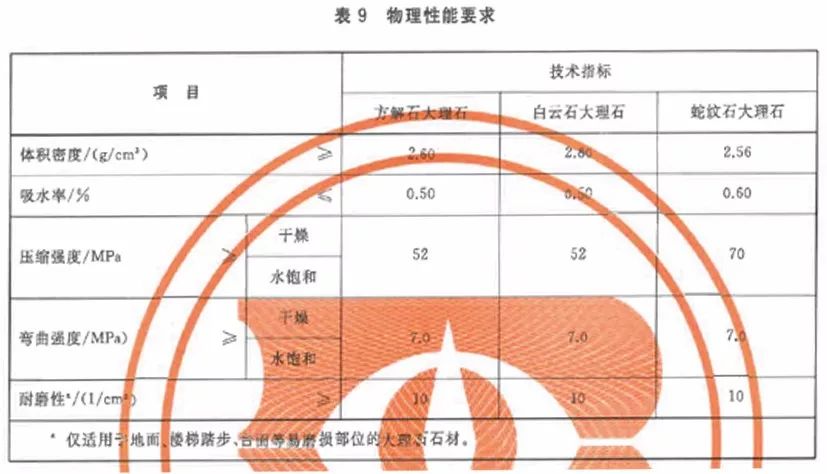
4. GB/T 19766-2016 Natural Marble Building Slab
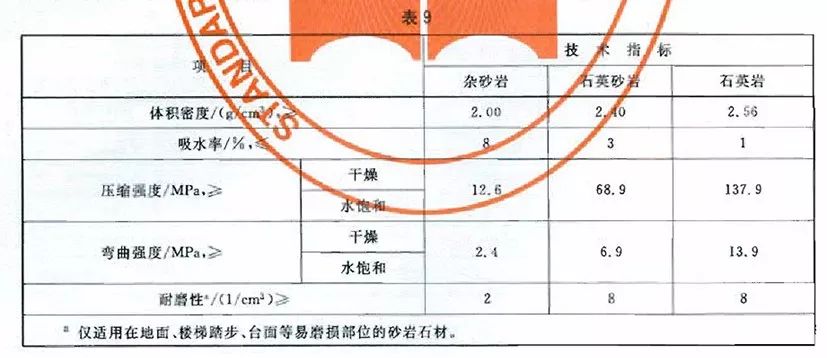
5. GB/T 23452-2009 Natural Sandstone Building Slab
5.4 Physical properties
The physical property indexes of natural sandstone building board shall conform to the provisions in Table 9. If the project has special requirements for the physical properties of natural sandstone building boards and the project, it shall be implemented according to the requirements of the project.
6. GB/T 18601-2009 Natural Granite Building Slab
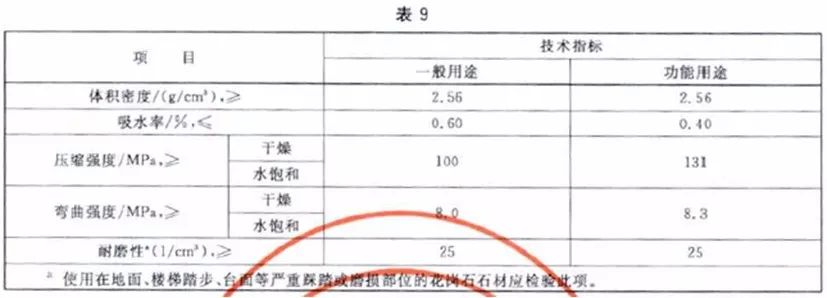
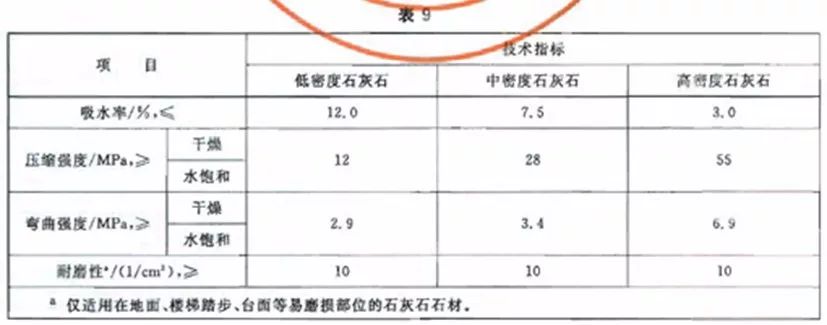
7. GB/T 23453-2009 Natural Limestone Building Slab
5.4 Physical properties
The physical properties of natural limestone building slabs shall conform to the provisions of Table 9. Where the project has special requirements for the physical properties and items of natural limestone building slabs, these shall be implemented in accordance with the project requirements.
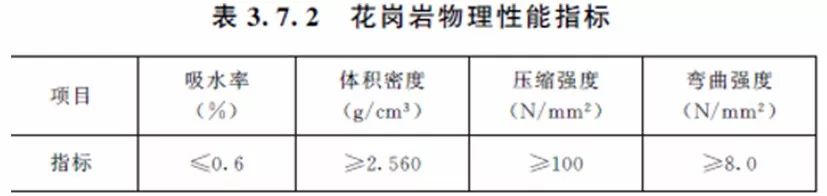
8. DGJ 08-56-2012 Shanghai Technical Code for Curtain Wall Engineering
10.4.2 The water absorption of granite shall not be greater than 0.6%, and that of marble shall not be greater than 0.5%.10.4.3
10.4.3 The bending strength of granite slabs shall not be less than 8.0 N/mm2, that of marble not less than 7.0 N/mm2 and that of other stones not less than 6.0 N/mm2, as tested by a statutory testing agency.
9. TDG/TJ 08-2134-2013 Technical Code for Application of Stone in Building Decoration Engineering of Shanghai
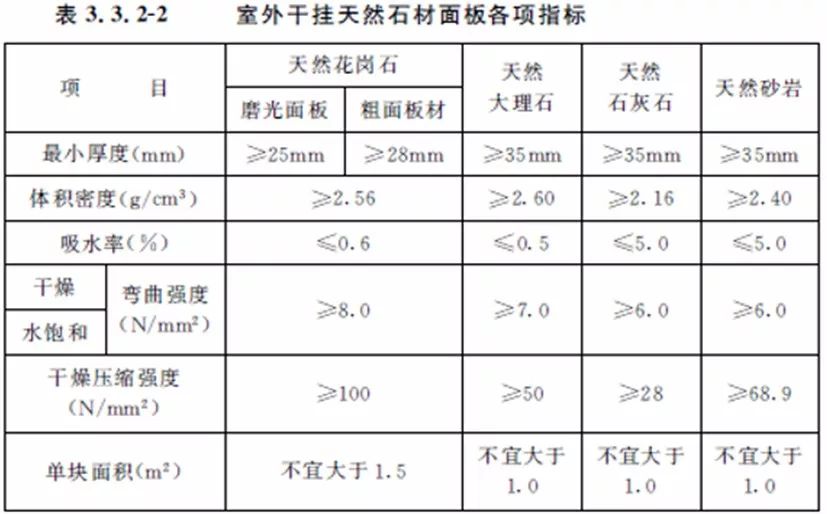
Note: The frost resistance coefficient of natural stone curtain wall panels with frost resistance requirements shall not be less than 80%.
10. DB 29-221-2013 Technical Code for Curtain Wall Engineering of Tianjin
3.6.1 The stone panel shall be made of granite, marble or sandstone, and its frost resistance coefficient shall not be less than 0.8, and its water absorption shall not be greater than 0.6%.
3.6.5 In dry state, the average value of bending strength test of granite panel shall not be less than 10.0 N/mm2, and the standard value of bending strength shall not be less than 8.0 N/mm2; When the height of curtain wall exceeds 100m, the average value of bending strength test of granite panel shall not be less than 12.0 N/mm2, and the standard value of bending strength shall not be less than 10.0 N/mm2. The average value of bending strength test of other types of stone shall not be less than 5.0 N/mm2, and the standard value of bending strength shall not be less than 4.0 N/mm2.
11. DB11/T 512-2007 Technical Specification for Stone Application of Beijing Building Decoration Engineering
12. GB/T 21086-2007 Curtain Wall for Building
7.2.1.5 Stone panels shall conform to the requirements of Table 46.
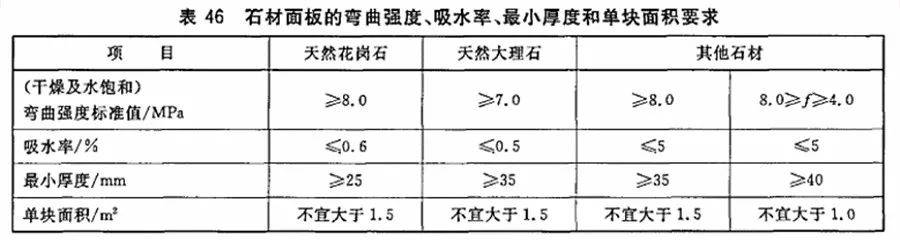
7.2.1.6 For the stone panel with the standard value of bending strength less than 8.0 MPa, additional structural measures shall be taken to ensure the reliability of the panel.
7.2.1.7 In severe cold and cold regions, the frost resistance coefficient of stone panel for curtain wall shall not be less than 0.8.
7.2.1.8 Stone surface should be protected. For stone panels in serious air pollution or acid rain environment, appropriate protective products should be selected to protect the stone according to the type and degree of pollution of pollutants and the mineral chemical and physical properties of the stone.
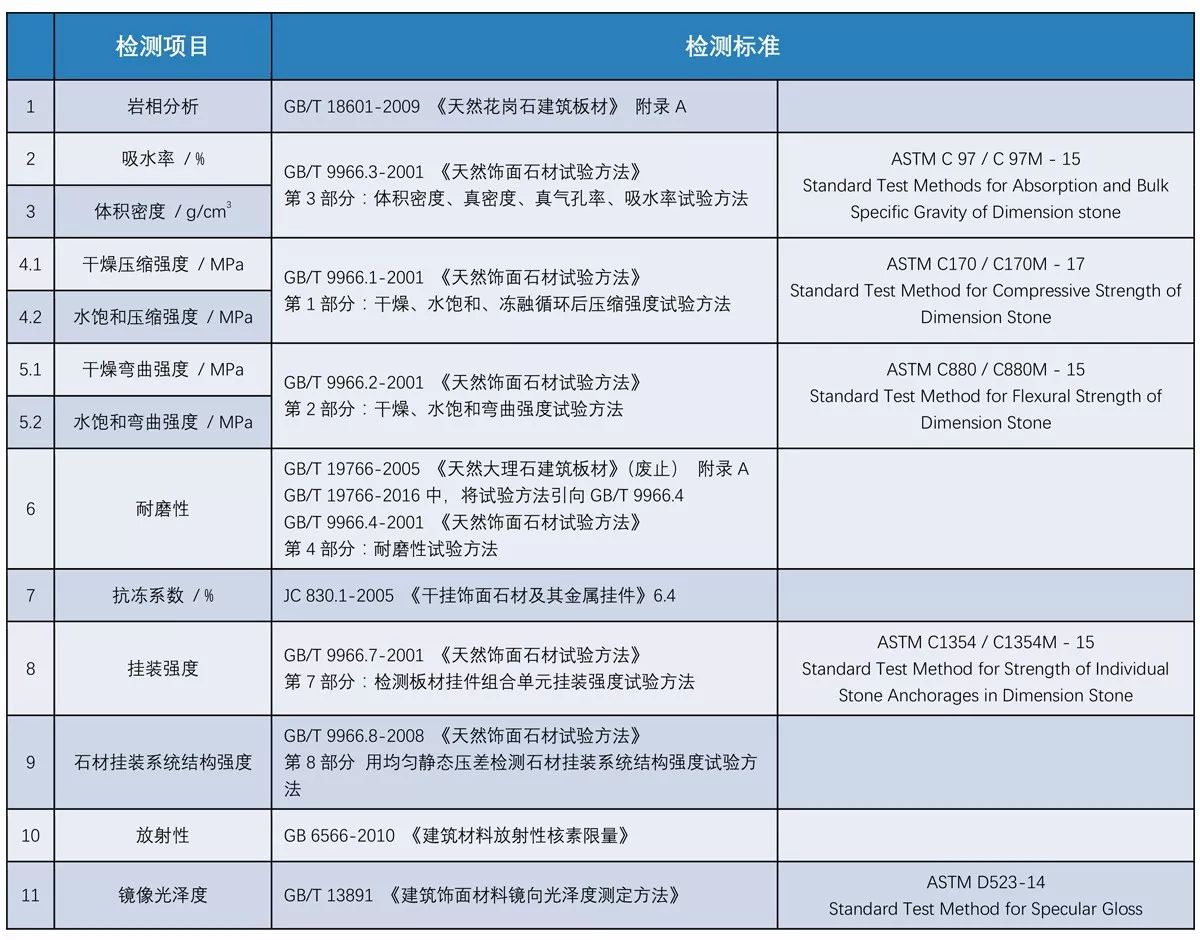
Relevant specifications for physical property test of stone are as follows:
6
Stone surface protection
Excerpts from the relevant specifications are as follows:
1. DG/TJ 08-2134-2013 Technical Code for Application of Stone in Building Decoration Engineering of Shanghai
3.9.2 Protective materials shall meet the following requirements:
1 The protective agent used for natural stone shall conform to the provisions of the current national standard Natural Stone Protective Agent for Architectural Decoration (JC/T 973).
2. The stone protective agent shall be provided with a factory certificate and an instruction manual. The imported stone protective agent shall be provided with a commodity inspection report and a certificate of origin.
3. Organosilicon and organofluoro-silicone protective agents with good permeability and air permeability should be selected as protective agents. The water resistance, alkali resistance, acid resistance and permeability of the protective agent should be taken as the main technical indexes.
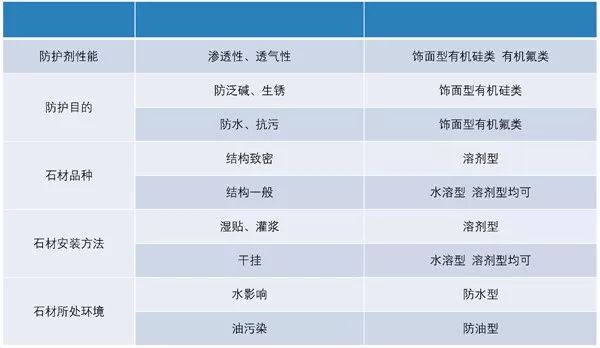
4. The protective agent shall be reasonably selected according to the type of stone, the environment in which the stone is used, the installation method of the stone and the protective design requirements of the stone.
5. The stone protective agent shall be sampled and tested when it enters the site, and the protective test shall be carried out when it is used.
6 When the protective agent is used on the bottom of the ground stone, its compatibility with the cement bonding material shall be ensured.
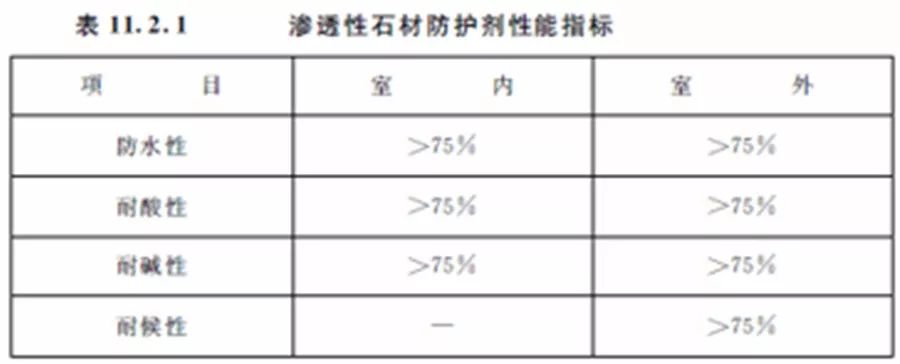
11.2.1 The selection of stone protective agent shall meet the following requirements:
1 The protective agent varieties, protection methods and technical requirements selected for the protective treatment shall form technical documents when the stone decoration project is determined. The document shall include the brand, model, performance requirements and painting process of the protective agent.
2 Permeable stone protective agent shall be used for indoor and outdoor stones, and the performance index of the protective agent shall conform to the provisions in Table 11.2.1.
3. When the bonding method is used for construction, the stone shall be protected from six sides, but the bonding strength between the stone and the ground base shall not be affected after the protection, and the reduction rate of the bonding strength of the cement shall not be greater than 5%; the stone ground should be waterproof adhesive.
11.2.2 Stone protection construction shall meet the following requirements:
1. Before large area construction, the selected protective agent and the protected stone shall be subject to small sample test.
2. If there are rust spots, color spots, glue marks, oil stains, wax and other stains on the stone surface, special cleaning agent for stone should be used to remove them before protective treatment.
3. During the construction of protection, the stone must be completely dry. The stone should be dried by natural drying or manual blowing. It is not suitable to use the method of insolation or fire. When the surface temperature of stone is too high, it is not suitable to apply protective agent.
4. Stone protection operation shall ensure good ventilation, no rain, no dust, temperature above 5℃, relative humidity not more than 80%, outdoor construction wind not more than level 4, and away from fire sources when applying solvent protective agent.
5. When the surface of granite, limestone, sandstone and other stones is rough or the water absorption of stones is large, the stone protection construction must be carried out at least twice.
6. When the protective agent is applied, all kinds of repair, grooving and special surface treatment of the stone shall be completed. The size shall meet the design requirements.
7. For the stone with reinforced net on the back, check the bonding strength between the back net and the stone. If the bonding is firm, the back net may not be removed.
8. If the stone is cut or grooved and holed on site during installation, the protective agent must be reapplied to the cutting part, and the protective agent must be maintained for 24 hours before installation.
9. The stone coated with protective agent shall be kept away from water or rain during the curing period.
10 After protection, the plate shall reach the following specified curing time: when the ambient temperature is 5℃ ~ 10℃, the curing time shall be 7 days; when the ambient temperature is 10℃ ~ 18℃, the curing time shall be 5 days; when the environmental temperature is above 18℃, it shall be 3 days.
11.2.3 The quality standard of stone protection construction shall meet the following requirements:
1. The construction of the protective agent shall not change the original color, texture and luster of the stone, except that the special effect meets the design requirements.
2 The penetration depth of permeable protective agent into stone shall meet the requirements in Table 11.2.3.
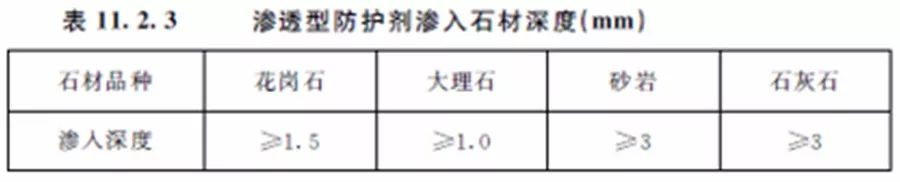
3. The protective agent shall be applied evenly without missing. After the protective agent takes effect, the stone shall be soaked and tested. The stone shall not be wet within 24 hours after being soaked in water.
4. The paved natural stone surface shall be free of uneven dryness and wetness of the stone surface due to uneven application and omission of the protective agent.
5 When the area of the single area is less than 1000 ㎡, the protective treatment shall be judged as qualified when the slight water permeability is ≤ 5% or the serious water permeability is ≤ 2%, otherwise it shall be judged as unqualified. When the area of the single area is more than 1000 ㎡, and the slight water permeability rate is ≤ 5% or the serious water permeability rate is ≤ 1%, the protection treatment shall be judged as qualified, otherwise it shall be judged as unqualified.
6. The paved natural stone surface shall be free of yellow spots, alkali return and other phenomena. The surface of the stone facing shall be free of traces of protective agent residues and dust. The stone coated with protective agent on the bottom surface shall be firmly bonded with the base course, and the special waterproof back glue for stone can be used.
2. DB11/T 512-2007 Technical Specification for Stone Application of Beijing Building Decoration Engineering
3.7.2 Protective materials
1 Classification of stone protective agent:
1) Classified by solvent type: water-based stone protective agent, solvent-based stone protective agent.
2) According to the function, it can be divided into waterproof stone protective agent, oil-proof stone protective agent and wet color stone protective agent.
3) According to the use position, it can be divided into decorative stone protective agent and bottom stone protective agent.
4) according to the main components, it can be divided into silicate stone protective agent, resin stone protective agent, silane siloxane stone protective agents, organic fluorine stone protective agents and fluorine silicon stone protective agents.
2 The protective agent used for natural stone shall meet the provisions of the industry standard Natural Stone Protective Agent for Architectural Decoration (JC/T 973), and shall be provided with a factory certificate and instructions.
3 The selection of protective agent should be based on different stone varieties, and neutral protective agent should be used for marble protection and cleaning. The protective agent with permeability and air permeability should be used as the finishing protective agent, and the film-forming protective agent should not be used.
4 Protective agents shall be selected according to different functional requirements. When the stone is greatly affected by water, the waterproof protective agent with strong waterproof ability should be selected; when the oil pollution is large, the oil protective agent with strong anti-fouling ability should be selected.
5 When the stone protective agent enters the site, it shall be sampled and tested, and the protective test shall be carried out on the stone used to ensure the reliability of the on-site products.
6. Bottom surface protective agent shall be used to ensure that the reduction rate of bonding strength of cement is not more than 5%.
7 The special care materials used in stone engineering shall meet the design requirements.
3. DB 29-221-2013 Technical Code for Curtain Wall Engineering of Tianjin
3.6.3 The surface and groove of the stone panel shall be protected, and the protective liquid shall not contaminate the stone.
14.6.7 Stone protection shall meet the following requirements:
1. The quality of the protective agent shall conform to the provisions of the current industry standard Natural Stone Protective Agent for Building Decoration (JC/T 973);
2. The protective agent shall be provided with instructions for use, waterproof, alkali resistance, air permeability, permeability and weather resistance test reports, as well as compatibility test reports with sealant and anchoring adhesive;
3. The stone protective agent shall be selected reasonably according to the type of stone and the type of pollution source, and shall meet the design requirements;
4 Stone protection construction treatment shall be carried out in the factory;
5. Solvent-based protective agent shall be selected to meet the requirements of building fire protection;
6. Before the protective agent is applied, the stone panel shall be fully and naturally dried after all processing is completed; measures shall be taken to ensure that the protected surface of the stone slab is clean and pollution-free;
7. The protection work shall be carried out in a clean environment, and the temperature and humidity conditions shall meet the technical requirements of the protective agent;8
8. The stone slab after protective treatment shall not be drenched or exposed to water before the protective effect takes effect.
4. JCG/T 60001-2007 Technical Specification for Natural Stone Decoration Engineering
5.3.1.5 Protective agent
5.3.1.5.1 Decorative protective agent shall be used for dry-hanging stone, which shall conform to the technical requirements of JC/T 973 superior products.
5.3.1.5.2 Permeable protective agent shall be used for dry-hanging granite, marble and limestone with good air permeability; suitable protective agent shall be determined for dry-hanging sandstone on the basis of test according to actual needs.
5. GB/T 32837-2016 Natural Stone Protective Agent
4 Classification, naming and labeling
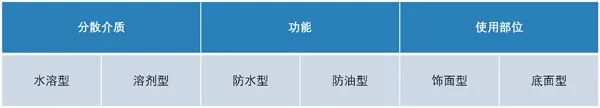
4.1 Classification
4.1.1 According to the dispersion medium, it can be divided into:
A) Aqueous type (SJ): protective agent with water as dispersion medium.
B) Solvent type (RJ): protective agent with organic solvent as dispersion medium.
4.1.2 Divided by function:
A) Waterproof type (FS): a protective agent that can prevent water and water-based pollutants from penetrating into the stone.
B) Oil-proof type (FY): a protective agent that can prevent oil and oily contaminants from penetrating into the stone.
4.1.3 According to the use position, it can be divided into:
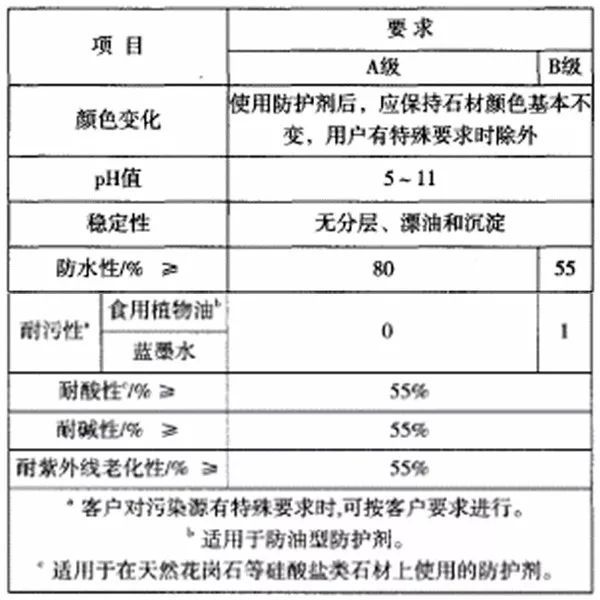
A) Finishing type (SM): protective agent for non-adhesive surface of stone. Finishing protective agent is divided into Grade A and Grade B according to water resistance and stain resistance.
B) Bottom surface type (DM): used as the protective agent for the sticking surface of stone.
5 Technical requirements
5.1 Finishing protectants shall be as specified in Table
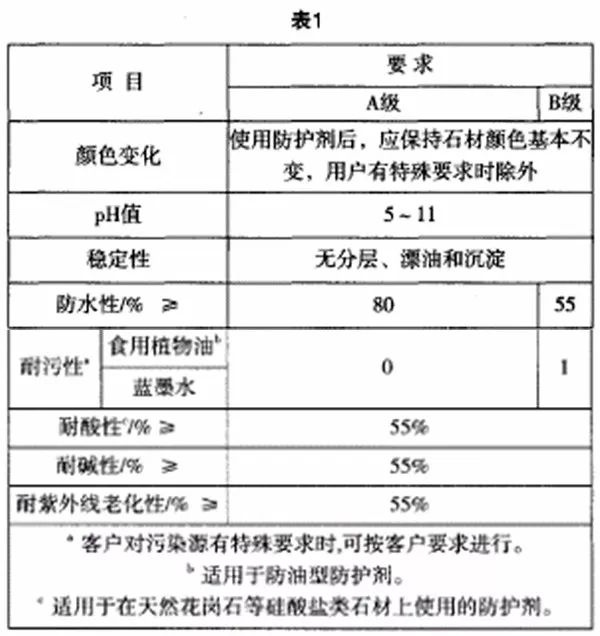
5.3 Volatile organic compounds (VOC) in water-based protective agent shall not be greater than 120g/L; benzene content in solvent-based protective agent shall not be greater than 0.3%, and the content of toluene, xylene and ethylbenzene shall be not greater than 5%.
6 Test method
6.1 Finishing type protective agent
6.1.1 Color change
Proceed as per A.3.1-A.3.4 in Appendix A.
6.1.2 pH value
Determine with precision pH test paper or pH meter.
6.1.3 Stability
Take two 10ml samples and put them into two test tubes respectively, put them on the opposite sides of the electric centrifuge, rotate them at a speed of 3000 R/min for 5 minutes, take out the test tubes, and observe whether there is stratification, floating oil and precipitation.
6.1.4 Waterproofness
Proceed as in Appendix A.
6.1.5 Stain resistance
Proceed as in Appendix B.
6.1.6 Acid resistance
Proceed as in Appendix C.
6.1.7 Alkali resistance
Proceed as in Appendix D.
6.1.8 Ultraviolet aging resistance
Proceed as in Appendix E.
6. JC/T 973-2005 Natural Stone Protective Agent for Architectural Decoration
4 Product Classification and Naming Mark
4.1 Classification
4.1.1 Classification by solvent type
4.1.1.1 Aqueous type (SJ): protective agent with water as dispersion medium.
4.1.1.2 Solvent type (RJ): protective agent with organic solvent as dispersion medium.
4.1.2 Classification by function
4.1.2.1 Waterproof type (FS): a protective agent that can prevent water and water-based pollutants from penetrating into the stone.
4.1.2.2 Oil-proof (FY): a protective agent that can prevent oil and oily contaminants from penetrating into the stone.
4.1.3 Classification by using part
4.1.3.1 Finishing type (SM): protective agent for dry-hanging stone (six sides) and wet-pasting stone decorative surface (including four sides).
4.1.3.2 Bottom surface type (DM): protective agent used to stick the bottom surface of stone.
5 Technical requirements
5.1 Finish type
5.1.1 When the decorative protective agent is used for stone protection, the color of the stone shall be kept basically unchanged, unless the user has special requirements.
5.1.2 The water resistance and stain resistance of the finishing protective agent shall conform to the provisions in Table 1.
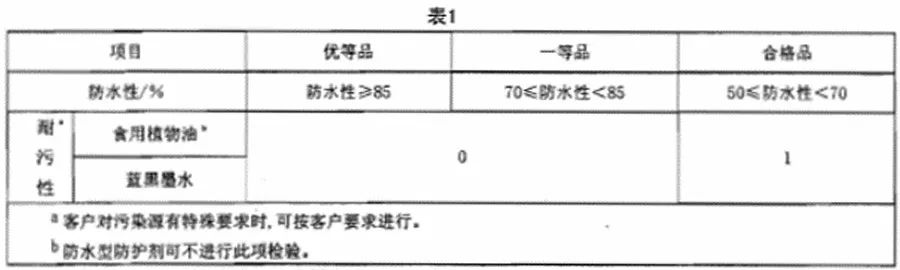
5.1.3 The pH range of the finishing water-based protective agent shall be 3 ~ 13.
5.1.4 The household registration stability of insomnia sexual intercourse shall be free of stratification, floating oil and precipitation.
5.1.5 The acid resistance and alkali resistance of the finishing protective agent shall be greater than or equal to 40%; the natural marble protection may not be tested for acid resistance.
5.1.6 The ultraviolet aging resistance of finishing protective agent shall be greater than or equal to 40%.
5.3 Limit of harmful substances of water-based protective agent
Volatile organic compounds (VOC) ≤ 200g/L.
5.4 Limit of Solvent-based Hazardous Substances
The content of benzene is ≤ 0.5%, and the content of toluene and xylene is ≤ 10%.
6 Test method
6.1 pH value
Determine with precision pH test paper.
6.2 Stability
Take two 10ml samples and put them into two test tubes respectively, put them on the opposite sides of the electric centrifuge, rotate them at a speed of 3000 R/min for 5 minutes, take out the test tubes, and observe whether there is stratification, floating oil and precipitation.
6.3 Waterproofness
See Appendix A.
6.4 Stain resistance
See Appendix B.
6.5 Decline rate of cement bond strength
See Appendix C.
6.6 Acid resistance
See Appendix D.
6.7 Alkali resistance
See Appendix E.
6.8 UV aging resistance
See Appendix F.
6.9 Impermeability
Place five stones of 150mm × 150mm × 20mm with the bottom and four sides protected according to A.3.1 to A.3.3 in Appendix A, with the bottom facing down, in a container (160mm × 160mm × 25mm wide side box with volume) containing cement mortar (cement and sand are prepared according to the ratio of 1: Lined with 240mm × 240mm plastic film), the cement mortar reaches about 1/2 of the thickness of the stone, and the exposed part of the stone side and the periphery of the container are sealed with plastic tape for seven days. Every other day, observe the color change of the sample surface and whether there is water spot, and record the abnormal surface condition.
6.10 Limit of harmful substances of water-based protective agent
Volatile organic compounds (VOC) shall be determined according to Annex A of GB 18582.
6.11 Limit of Solvent-borne Hazardous Substances
Benzene, toluene and xylene shall be determined according to Appendix A in GB 18581.
Summary of stone protective agent:
Classification of protective agents
Technical requirements for protective agent
(Extracted from GB/T 32837-2016 Natural Stone Protective Agent)
Principles for selection and use of protective agent
As for the content of stone, we will share these with you first, and please continue to look forward to the dry goods knowledge of other facades. Furst will continue to share with you